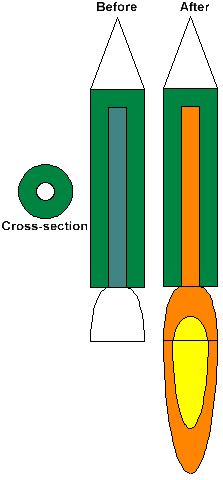Rocket Fuels- Solid vs. Liquid
There are two types of rockets in use today: Solid fuel rockets, and Liquid fuel rockets. How these two types of rockets work is very different. Each have their respective advantages and disadvantages.
Solid Fuel Rockets:
The first rockets invented were solid fuel rockets. Solid fuel rockets work by burning a solid substance that burns quickly but does not explode. One such substance would be the compound containing 72% nitrate, 24% carbon and 4% sulfur. This compound is very much like gunpowder, but due to the different proportions of the materials, it burns rapidly rather than exploding. When loaded into the rocket, the fuel is shaped as a cylinder with a tube drilled down the middle. After ignition, the fuel burns along the walls of this tube, gradually consuming the fuel until there is none left (see diagram)
Image courtesy of www.howthingswork.com
In the above diagram, the fuel is in green and the tube is in blue. Once ignited, the tube is shown in orange because it is burning. In addition to a tube shaped perforation, there can be other shapes used. For example, the fuel in the space shuttles SRB's or solid Rocket boosters is often drilled with a 11 pointed star shape. This increases the surface area that is currently burning, thus increasing the resulting thrust. A common description of the fuel used in the shuttles SRB's is this:
The propellant mixture in each SRB motor consists of an ammonium perchlorate (oxidizer, 69.6 percent by weight), aluminum (fuel, 16 percent), iron oxide (a catalyst, 0.4 percent), a polymer (a binder that holds the mixture together, 12.04 percent), and an epoxy curing agent (1.96 percent). The propellant is an 11-point star-shaped perforation in the forward motor segment and a double- truncated- cone perforation in each of the aft segments and aft closure. This configuration provides high thrust at ignition and then reduces the thrust by approximately a third 50 seconds after lift-off to prevent overstressing the vehicle during maximum dynamic pressure.
Advantages of Solid Rocket boosters:
- Simplicity. Since you are basically just putting a match to a pile of highly flammable material, Solid rocket boosters are very simple.
- Low Cost. The Materials used to create the fuel are relatively inexpensive.
- Safety. Assuming that the fuel was produced properly, there is no danger of explosion. It will simply burn until it is gone, and then stop.
In spite of these advantages, there are also several disadvantages to solid rocket boosters:
- Thrust can not be controlled. Once lit, it burns at a steady rate. You can not change this rate without changing the composition of the fuel used.
- Once ignited, the engine can not be stopped or restarted. Any method that might possibly halt the combustion of the fuel would be sure to destroy the remaining fuel.
To couteract these disadvantages, the Liquid fuel rocket was created.